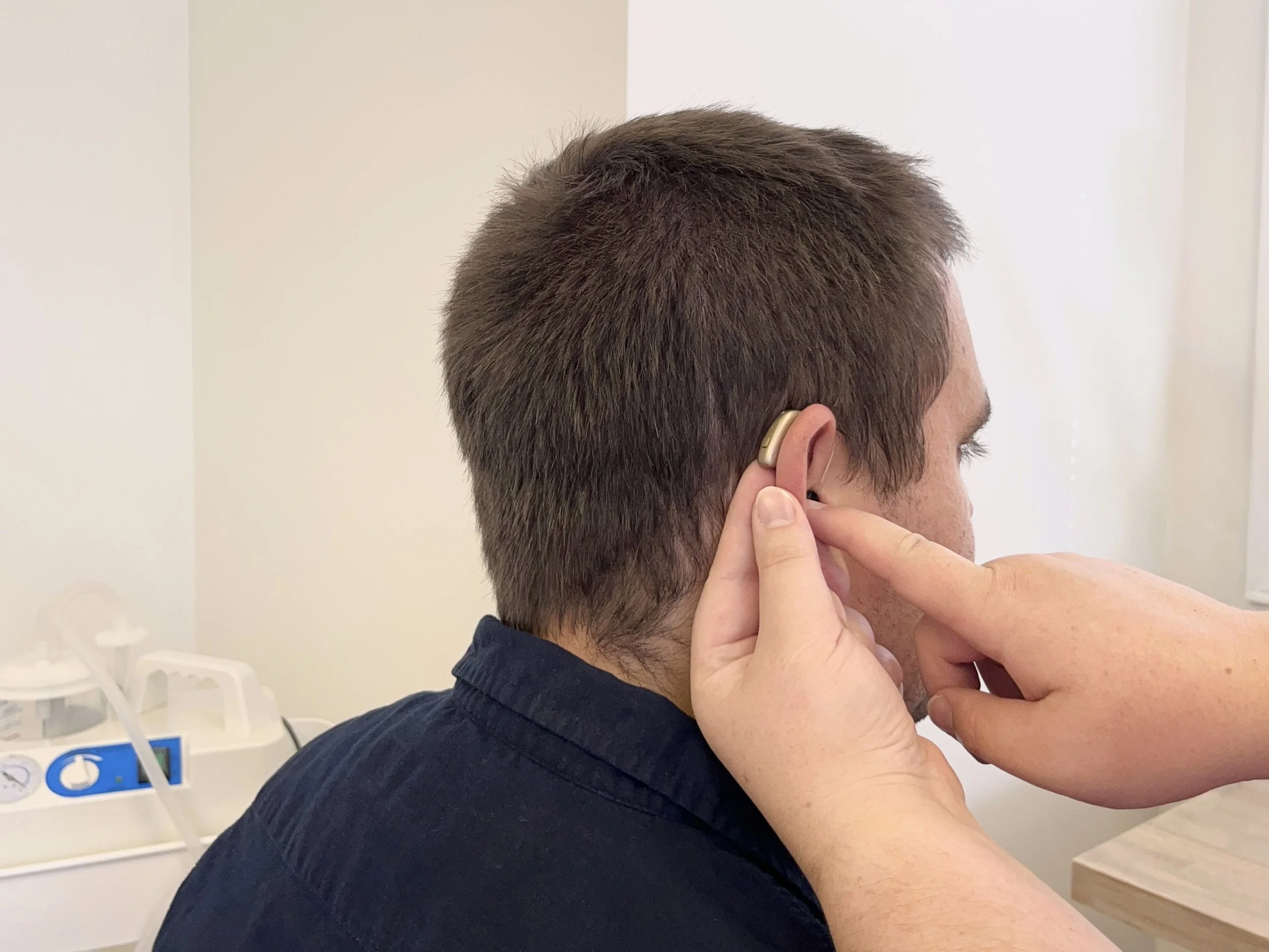
Comprehensive and Accurate Hearing Tests in Huntsville
Hearing connects us to the world around us — but hearing loss often happens gradually. Birdsong Audiology takes pride in providing comprehensive hearing assessments.
Hearing loss is incredibly common and can happen at any stage of life. Approximately 8% of children and teenagers in Canada experience some level of hearing loss. As individuals age, the likelihood of experiencing hearing loss rises significantly—38% of adults and more than 78% of seniors are affected.
At Birdsong Audiology, we offer thorough hearing assessments to detect hearing loss and recommend the best solutions for your lifestyle.
What to Expect At Your Hearing Test
Otoscopy
We use an otoscope to visually inspect the integrity of your outer ear and eardrum. We will remove any occluding ear wax prior to testing.
Tympanometry
Tympanometry is used to assess your middle ear function. This helps identify issues such as negative middle ear pressure, fluid build-up, and eardrum perforations.
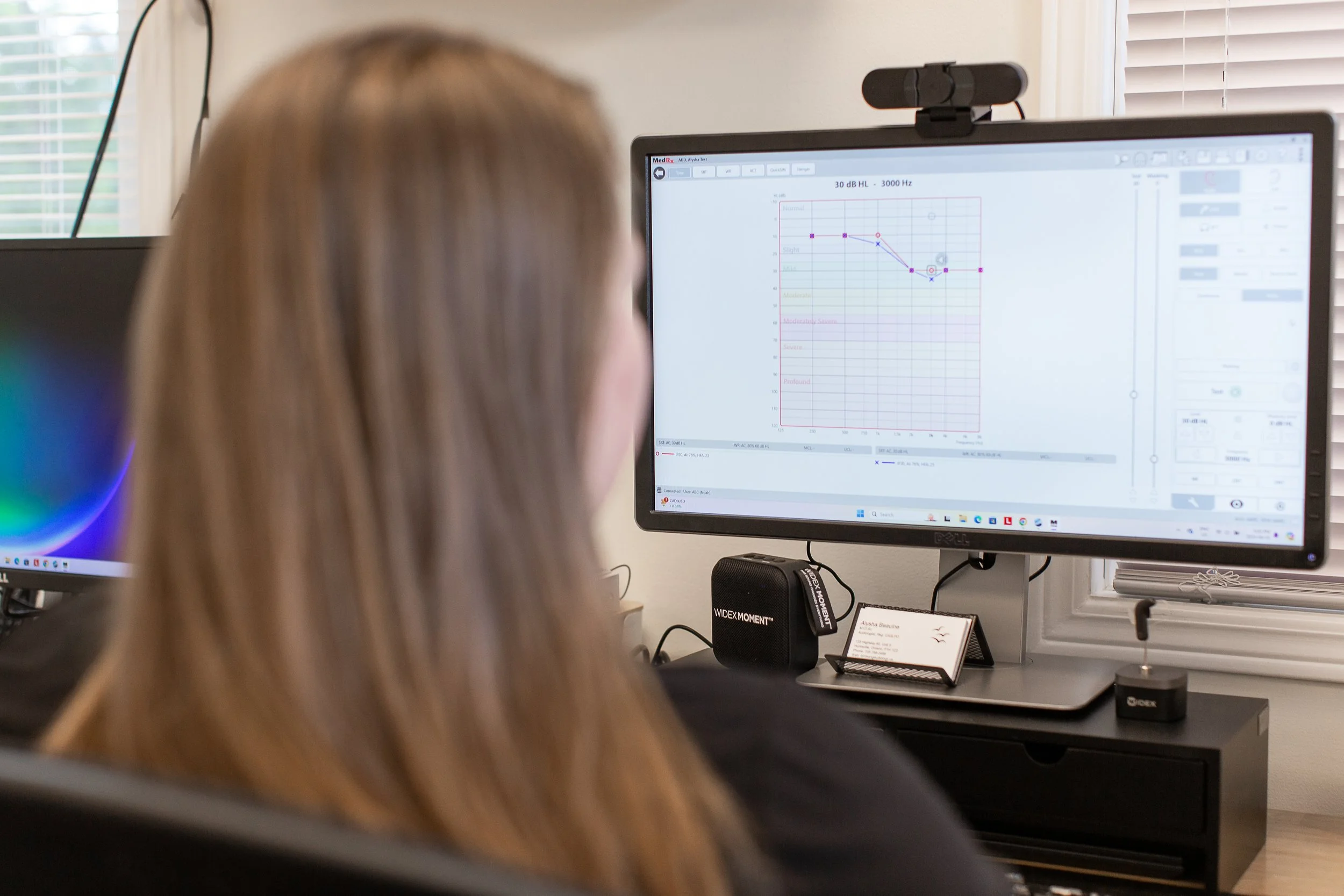
Pure-Tone Audiometry
You will listen for very quiet sounds at different pitches. This shows us your hearing thresholds, the softest sounds you can detect.
Bone Conduction
Bone conduction testing allows us to understand whether your hearing loss is conductive, sensorineural, or a mixture of both.
Speech Audiometry
Speech audiometry determines your ability to hear and understand words in a quiet environment.
Speech-in-Noise Test
Speech-in-noise testing determines how well you understand speech in background noise.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Yes! Many people are unaware of gradual hearing changes. A baseline hearing assessment helps track your hearing health over time.
-
Tinnitus - ringing, buzzing, roaring, or other noises in your ears or head
Mixing up words, especially in a crowded place
Feeling like other people are mumbling or muffled
Frequently asking for repetition
Asking people to speak louder or slower
Needing to turn up the volume of the TV or music
Hearing loss usually comes on slowly. If you are over the age of 60 or regularly exposed to noise, you should check your hearing every year.
-
Common causes of hearing loss include:
Impacted ear wax
Conditions of the middle ear, such as otosclerosis
Inner ear conditions, such as Ménière's disease
Ototoxic medications
Noise exposure
Head injury
Presbycusis (age-related hearing loss)
-
Hearing assessments are $140 and are privately paid (not covered by OHIP). Many extended health insurance plans include audiology coverage — check with your provider!
-
During your hearing assessment, our audiologist will use advanced equipment to test your hearing across a range of frequencies. The test is non-invasive, painless, and takes about an hour.
-
Some hearing losses are temporary (like earwax blockages), while others are permanent. A professional hearing test identifies the type and degree of hearing loss.
-
There are three types of hearing loss:
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
A sensorineural hearing loss is the most common kind of hearing loss. It can be caused by excessive noise exposure, ototoxic medications, and/or aging. This type of hearing loss occurs from damage to the inner ear and is permanent.
Conductive Hearing Loss
A conductive hearing loss occurs from dysfunction or blockage in the outer or middle ear. It can occur from excessive ear wax, middle ear issues such as fluid build-up behind the eardrum, or other middle ear conditions.
Mixed Hearing Loss
A mixed hearing loss occurs when both a sensorineural and conductive hearing loss occur at the same time. For instance, if you have ear wax blocking your hearing and an underlying age-related hearing loss, that would result in a mixed hearing loss.